
一种多肿瘤培养芯片(MTC-chip)以模拟实体瘤及动态流体运输,用于更好地研究纳米粒子(NPs)的体内渗透。
Introduction
通过提供抗降解保护、增强通透性和滞留效应的纳米颗粒(NPs)的快速发展显著改善了药物转运的肿瘤治疗。由于传统的细胞模型无法完全复制体内的生理环境(如缺乏流体流动、脉管系统、细胞外基质等),因此体外和体内研究之间在细胞摄取效率和纳米颗粒的毒性方面仍然存在巨大差异,纳米医学在临床试验中仅取得了有限的治疗效果。
- 一些纳米颗粒很容易聚集或沉淀,从而增加粘附细胞表面纳米颗粒的浓度。
- 静态模型不能反映动态流动系统下纳米颗粒的渗透特性,需要将模拟的肿瘤间隙流集成到三维肿瘤评估系统中。
- 剪切应力会导致细胞损伤并改变纳米材料的吸收,需要考虑减少微流控装置中的剪切应力。
在本文中,作者制造了一个多肿瘤培养芯片(MTC-chip)用于生产大量三维肿瘤球,并在MTC芯片中加入了动态用药系统,以评估在间接剪切力下乳腺癌MCF-7球体中介孔二氧化硅纳米粒子(MSN)的细胞摄取。最近,MSNs已被用作癌症治疗的多功能纳米递送系统,其生物降解性以及相容性已在动物研究中得到证实。作者证明了MTC-chip研究MSNs渗透的能力,并发现:
- 在相同剂量下,连续给药优于瞬时给药;
- 三维动态条件下,球体内细胞摄取的尺寸效应小于二维静态模型;
- 透明质酸酶(hyaluronidase, HAase)增强了大尺寸MSNs在肿瘤球中的渗透。
Microfluidic Chip Design and Operation
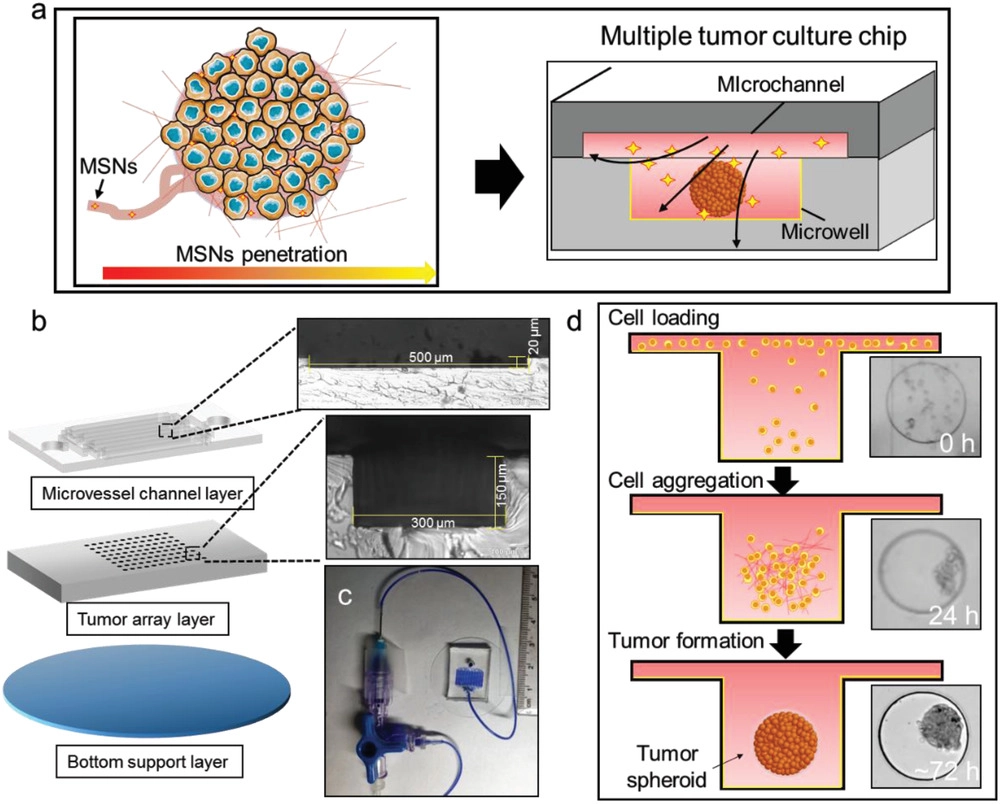
- (a)用于NPs渗透研究的MTC-chip。
- (b)三层微流控装置的示意图与光学显微图片。微通道的深度大约20 μm,微孔深度大约150 μm。
- (c)整个装置照片。
- (d)芯片上三维培养流程。
Microfluidic Cell Culture
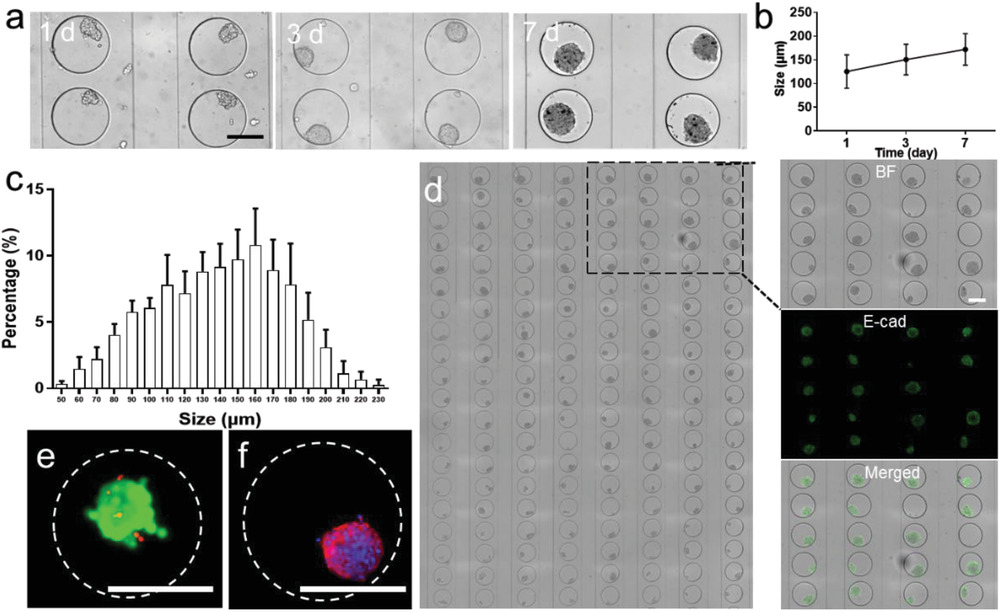
- (a)第1、3、7天培养的MCF-7肿瘤球的光学图像和尺寸。
- (b)芯片上三维肿瘤的尺寸生长。
- (c)芯片上三维肿瘤的尺寸分布。
- (d)芯片上160个MCF-7肿瘤的白光图和20个充满E-钙黏蛋白(E-CAD)染色肿瘤球的微孔的图像分析。E-CAD与保持MCF-7细胞-细胞连接有关,可以发现处于高水平表达。
- (e)用Calcein-AM/PI的活/死(绿/红)染色可视化肿瘤细胞的荧光图像。
- (f)F-肌动蛋白(红)和核(蓝)染色以展示细胞骨架的荧光图像。上述结果证实了微流控系统制备的肿瘤球的高活力和完整性。
Effect of the Route of Administration on NPs Penetration
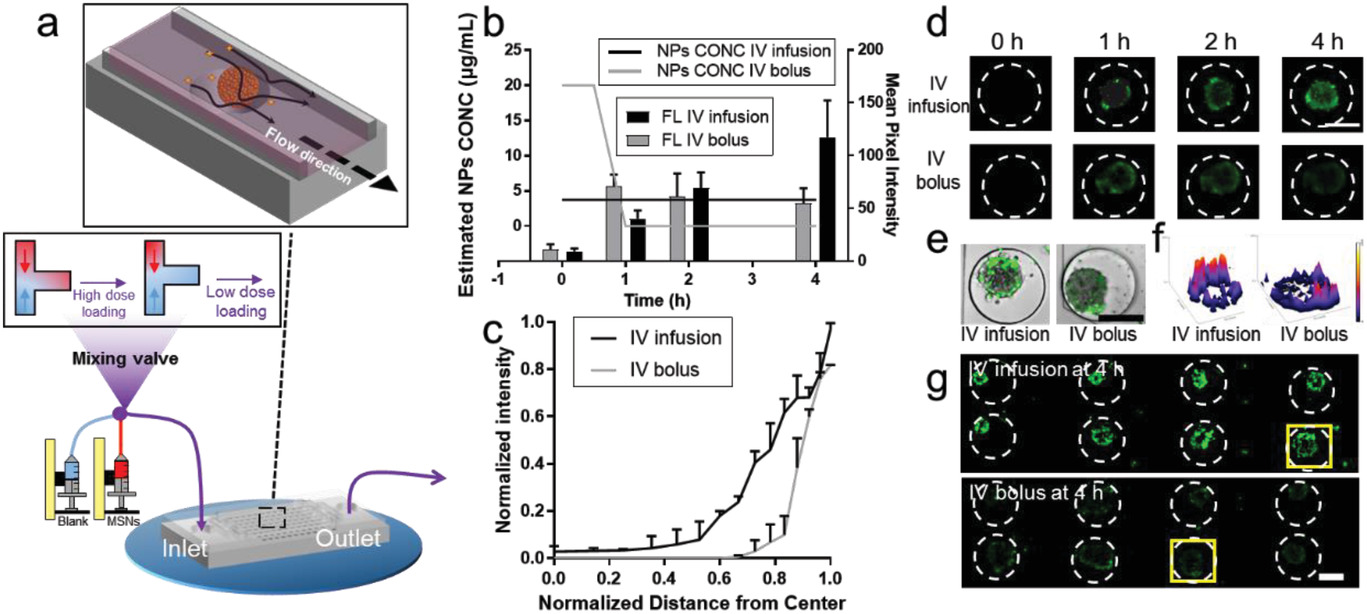
- (a)在带有三通混合阀入口的芯片上应用不同的MSNs给药途径的透视图。
- (b)通过静脉输液或静脉注射,估计芯片上微通道中MSN90的浓度(CONC)以及MSNs在肿瘤球中的粒子动力学。
- (c)NPs的归一化荧光强度分布与肿瘤球中心距离的关系。
- (d)MSN90在一个肿瘤球中通过静脉输液或静脉注射渗透的时间推移图像。
- (e)MSN90在一个肿瘤球中通过静脉输液或静脉注射渗透的合并图像。
- (f)基于(g)的荧光图像绘制的一个MCF-7肿瘤球的表面图像。
- (g)MSN90在八个肿瘤球中,经不同给药途径后的细胞摄取情况。由此可知持续给药可导致在肿瘤球中更深更强的渗透。瞬时给药与MSNs在肿瘤球中的保留关系不大,而连续给药则有利于MSNs的积累。
Effect of the Size of MSNs on NPs Penetration after a Single Dose Continuous Administration NPs Delivery
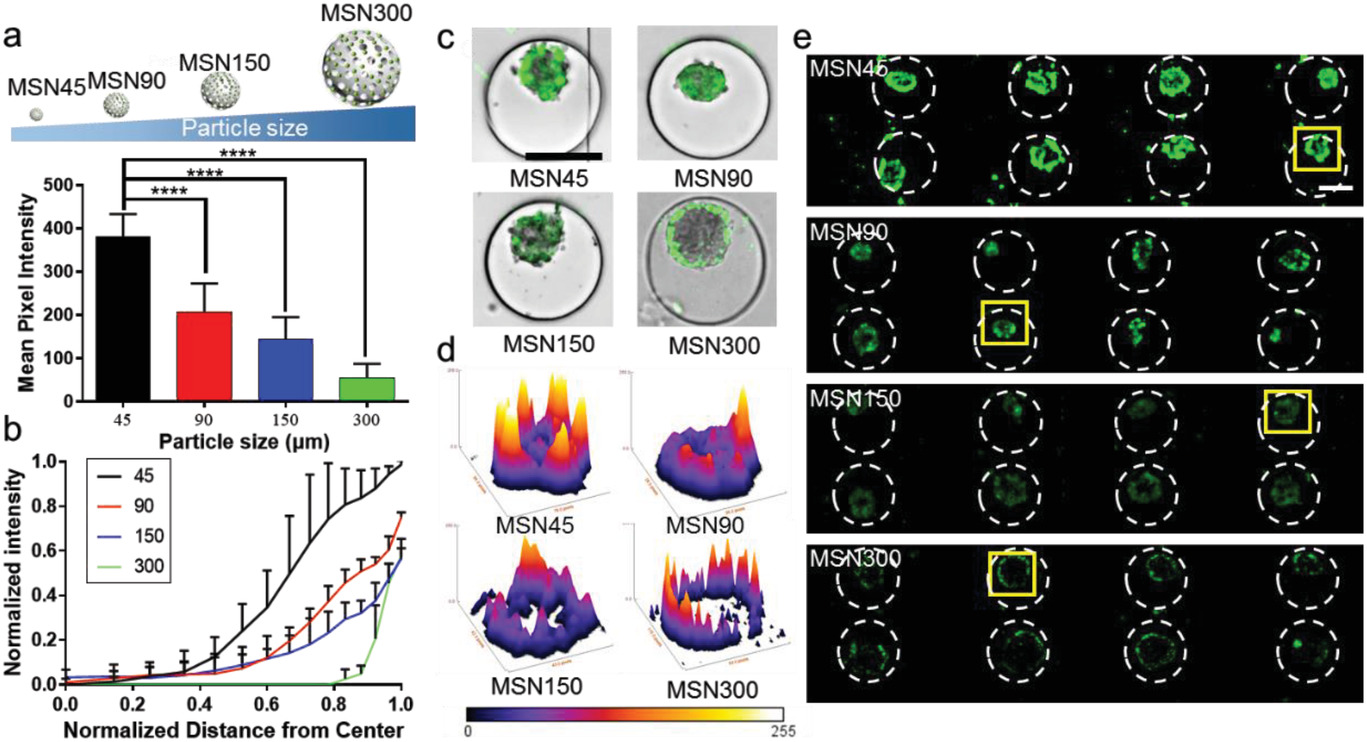
- (a)MSNs内化后细胞的平均荧光强度。
- (b)MSNs加载后NPs的归一化荧光强度分布与肿瘤球中心距离的函数。表明与大尺寸的MSNs相比,小尺寸的MSNs更倾向于在肿瘤球中积累。
- (c) MSNs在一个三维肿瘤中渗透的合并图像。
- (d)基于(e)的荧光图像绘制的一个MCF-7肿瘤球的表面图像。
- (e)八个肿瘤球中不同尺寸MSNs的细胞吸收。 表明较小的MSNs在4小时内更接近中心,而大尺寸MSNs无法有效扩散到三维肿瘤中。但在静态孵育下的二维/三维细胞中,细胞几乎不可能摄取任何大尺寸的MSNs。
Effect of ECM Pretreatment of Tumor Spheroids on MSN300 Accumulation
尽管直径较大的纳米载体渗透性较差以及细胞摄取率较低,但更高的载药量和更好的稳定性使研究人员不愿放弃这些大尺寸纳米载体。如今,各种方法如NPs的表面共轭已被应用于增强这些大尺寸NPs的肿瘤渗透;与基质调节剂共同给药,可以通过药理作用调节肿瘤微环境,已被广泛应用于临床研究中增强肿瘤渗透。该微流控装置可以在一定程度上构建三维肿瘤及其微环境,可用于测试此类药物。

- (a)实验设计示意图。在三维肿瘤形成后,MCF-7肿瘤球在加载MSNs前用不同的ECM修饰剂处理2天。
- (b)MSNs内化后细胞的平均荧光强度。透明质酸酶可作为ECM降解酶并降解水凝胶,显著增强MSN300的肿瘤渗透。
- (c)MSNs加载后NPs的归一化荧光强度分布与肿瘤球中心距离的函数。
- (d)MSNs在一个三维肿瘤中渗透的合并图像。
- (e)基于(f)的荧光图像绘制的一个MCF-7肿瘤球的表面图像。
- (f)八个肿瘤球对MSNs的细胞吸收。由于报道中氯沙坦和法舒地尔可以增加体内NPs的积累,由此假设透明质酸酶对ECM有直接影响,这在MTC芯片中可能更有效,而氯沙坦和法舒地尔只能对ECM产生间接影响。
Conclusions
提出了一种高通量、仿生和动态的给药系统,可以在芯片上生产许多MCF-7肿瘤球。三维多细胞肿瘤球(3D-MCTS)、ECM和间质液系统被成功集成到微流体平台中,可以提供更接近TME的生理条件,用于探索NPs渗透。以前的研究已经通过微流控技术有效地实现了三维培养,但很少有人能够在这种系统中进行NPs的渗透以及动态用药下NPs的细胞摄取。作者证明了:
- 给药途径可以决定MSNs的渗透率,纳米药物的连续给药导致肿瘤球中NPs的积累比瞬时给药更大;
- 尺寸对MSNs细胞摄取的影响也适用于 3D 流动条件。然而传统的静态孵育系统被认为夸大了MSNs大小对细胞摄取的作用;
- 透明质酸酶可直接降解肿瘤胶原含量,增强大尺寸MSNs在肿瘤球体中的渗透,而这种改善可能会被MTC芯片检测到,因为芯片上的TME系统可以部分复制体内微环境。
Reference
Zhuang J, Zhang J, Wu M, et al. A Dynamic 3D Tumor Spheroid Chip Enables More Accurate Nanomedicine Uptake Evaluation[J]. Advanced Science, 2019, 6(22): 1901462.



